Decompensated Cirrhosis:
- etiology:- HE: prior hospitalizations w/ HE: y/n
- rifaximin, lactulose for goal 3-4 BM
- EV: last EGD:
- Ascites/SBP:
- HCC: Liver US
- PVT: Liver US
- transplant: defer workup to hepatology
Summary
- Background: Cirrhosis distortion and formation of regenerative nodules
- Complications of Cirrhosis: VIBES: volume (ascites, HRS), Infection (SBP), Bleeding (Variceal bleeding), Encephalopathy, screening
- Goals of Management:
- Prognosis:
Complications:
General Management
1. Discontinue alcohol – baclofen (reduce alcohol consumption & craving)
2. Renal perfusion (NSAIDs, ACEs, ARBs) lower arterial BP associated w/ lower survival (propranolol, ACEis, bbs). “cirrhosis cures htn” MAP < 82 2 yr survival 20%, MAP > 82 2 yr 70%
3. Txt underlying liver disease
4. Sodium restriction: fluid restriction Na < 120 mEq/L
5. Diuretics: Spiro/Furosemide 100:40, titrate > 3 to 50 days. Stage 1 100:40 stage 2 200:80; stage 3 300:120 stage 4 max: 400: 160. Paracentesis 6 to 8 g/L removed.
Liver transplant + shunt. Therapeutic paracentesis & TIPS: transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt
Chronic albumin, SGLT2
Cirrhosis etiology coggle it
Umbilical hernias: repair umbilical hernias, elastic/Velcro abdominal binders reduce pain
Hyponatremia, variceal bleeding (beta blocker, ligation), carcinoma (hepatocellular, ultrasonography), HE grade 1, 2, 3, 4 lactulose, rifaximin. Cirrhosis associated immune deficiency: UTIs, pneumonia, SBP, cryptococcal meningitis
Prognosis
Compensated Cirrhosis: compensated cirrhosis > 12 yrs.
Decompensated cirrhosis: VIBES: < 6 mo. Decompensated cirrhosis Child-Pugh >12 MELD > 21
Predictive Models
- Child Pugh:
- MELD score:
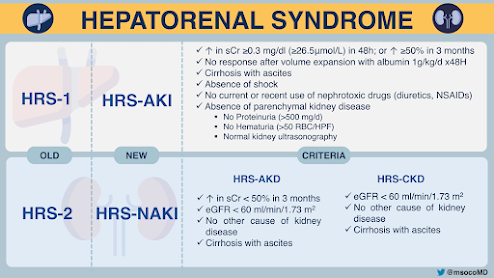
HEPATORENAL SYNDROME
rise in cardiac output and fall in systemic vascular resistance
holding diuretics and giving albumin worsens hepatorenal syndrome, 1 gram per kilogram per day x48 hours
albumin and holding diuretics with response more likely prerenal
Treatment
Antihypertensives discontinued in all patients with hepatorenal syndrome
ICU:
- norepinephrine IV continuous gtt (0.5 to 3mg/hr) goal raising MAP by 10mmHg albumin given as intravenous bolus (1 gram/kilogram per day [100gram meximum])
non-ICU
- terlipressin therapy (analogue of vasopressin)
- combination of midodrine, octreotide, and albumin
fail therapy - TIPS
MELD score - liver translant

.png)


Comments
Post a Comment