Introduction
hello and welcome to another video at
the pharmacist Academy whoa how to
monitor patients on vancomycin
now vancomycin is a very important
antibiotic simply because it has
potential to cause renal failure
now this renal failure is usually
preventable by monitoring the patient's
trough levels so in this video we are
going to discuss how to dose these
patients initially how to modify the
doses and how to monitor these patients
while they're taking the medication
Background of Vancomycin
now to begin I wanted to provide a
little background of vancomycin
vancomycin is a glycoside antibiotic and
it mostly covers gram-positive organisms
right includes an Mrs a B number one
concern and the number one use really
for vancomycin and Clostridium difficile
infections c diff in that case we use
the oral form of vancomycin now the
medical users are listed here for your
information and vancomycin is usually
used also when a patient has a
penicillin allergy so they can get let's
say any type of penicillin
cephalosporins or whatever the case is
and you need to cover gram positive then
vancomycin is usually your go-to
medication now once these patients are
Initial Dosing
started on vancomycin they are usually
start on the initial dosing right and
very few patients received a load and
dose of this medication now that those
are frequency is based on actual body
weight okay regardless if the patient is
obese or not and renal function also
plays a row now for patients who are
critically ill right like patients with
endocarditis patients with meningitis
they usually receive an IV loading dose
before they start the maintenance dose
and this is simply to increase the
amount of vancomycin and the blood right
away
and then the patient will receive you
know in amman maintenance doses of the
medication and this is usually done in
the IDI or the emergency room they give
the patient a one-time dose of this
medication and then they send the
patient up to the unit now as I
mentioned already you use actual body
weight for obese patients also now those
modifications after the initial dosing
are based on the trough levels which I
will talk about a little bit more as we
go
institutions may also create something
something known as a docent table for
Dosing Table
the initial dose and of vancomycin and
as you can see here they have the actual
body weights here right and depending on
the cran and Clarence you get a dose
plus of frequency so every institution
may have their own way of doing this but
they usually follow the same idea of you
Dosing Schedule
know the same dosing right like 15 to 20
milligrams per kilogram and it could be
given every eight hours every 12 hours
or every 24 hours
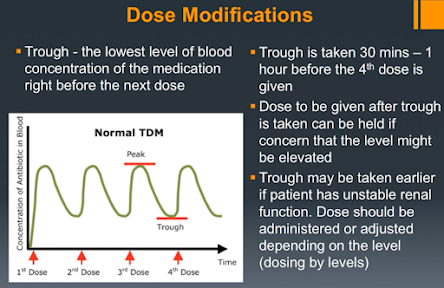
Trough
now once the patient is started on this
initiative those what you want to do is
monitor the patient right because we
want to prevent any renal toxicity from
the medication so we look at something
known as a trough now a trough level is
simply the lowest level of blood
concentration of the medication right
before the next dose so as soon as you
give a dose here right the amount of
vancomycin and the blood increases right
away but over time it starts to drop
okay now once it gets here this is the
lowest point of guy right the lowest
amount of vancomycin you had in the
blood before you gave the second dose
and brought it back up now when it's up
here it's a peak as you can see here now
the trough is usually taken 30 minutes
to one hour before the fourth dose of
the vancomycin is given and this is
simply done because we want to make sure
the medication is in steady state and I
usually take
about three doses for us to achieve that
now once you're in study state you could
take the vancomycin 30 minutes of one
hour before the next dose right well
there's the four of those the fifth dose
the six those you could get the loved
one it's appropriate but we usually want
to do it right before the fourth dose
now the dose to be given after the
trough right so if you take the tribe
you draw the blood level right but right
after you draw the blood level you can
actually give a dose okay but in certain
cases they may hold the dose because
they are really concerned at the trough
level might be a little higher it might
be a little higher so the more
medication the more vancomycin the
patient get and the patient is unable to
clear it the higher the trough levels
will be and that will increase the
patient's chance of developing renal
toxicity now the chart maybe taken
earlier if patient has unstable renal
function so you don't even need to wait
so it's steady state right the patient
has renal like bare renal function you
could check the trough earlier you don't
need to give the patient three doses
first in order to check right you could
do this and this is what we call dose
and a patient by level I'm gonna go
through some patient cases as we go on
so you understand is more now those
modifications once again this is usually
done right you only do those
modifications based on the trough level
and a trough level for skin and
soft-tissue or other infections are
usually 10 to 15 and for you know sepsis
bacteremia st my light is and the car
diet is that's all 15 to 20 now based on
the trough level the dose should be
increased if patients trough is lower
than the target level right the dough
should be decreased if patients Chavez
higher than the target level if patients
renal function is worsening all right so
that those could be skipped in this case
also remember that
you don't need to give the dose if you
think that the renal function may worsen
or it's not that stable now when you're
monitoring patients on vancomycin or
before you verify a vancomycin order or
you're waking up a patient on vancomycin
before you go around and you want to
consider each of the following the
trough already discussed but we're gonna
go through each one of this so the way
Weight
those are frequency increases the the
weight right it proportionally increases
with the weight they go up at the same
time right they both go up so example
assuming the age and renal function is
the same in this case right patient a
may receive patient a is 50 kilos and
will receive one gram every 12 hours of
vancomycin but patient B is 100 kilos I
may receive 1.5 grams every 12 hours
right so because of the weight
difference the patient weighed more
received more of the vancomycin and
sometimes the frequency you know that
patient can also receive it more often
so take that into consideration age also
plays a role when it comes to those in
these patients so frequency and/or dose
make the crease with increased age and
this is because we tend to associate all
the patients with sub-optimal renal
function right they don't have the best
kidneys they may not be clearing this
medication now assuming the weight is
the same patient a is 70 years old and
will receive one gram once daily and
patient B is thirty years old and will
receive one gram every 12 hours okay now
Serum Creatine
we also want to monitor these patients
right and when we're monitoring these
patients we look at the serum creatinine
so before you verify let's say a
vancomycin order you want to look at the
some crowning right as the most
important thing you want to look for now
you want to make sure you evaluate the
some cran and trend don't just look at
the current level so let's say today was
January 4th
and I see this level of 0.8 I'm not just
gonna focus on 0.8 I'm not gonna just
assume this is the baseline you have to
look at the trend to notice the baseline
right so the patient's baseline was
actually 0.3 when they first came in and
as you can see is slowly increasing
right now once you notice that it's
increasing you could use your clinical
judgment
okay the renal function might be
worsening so maybe when this patient is
starting this vancomycin right they
shouldn't be too aggressive right they
should be a little cautious because the
renal function might worsen now if a
renal function is worsen and consider
lowering the dose and or just and/or
adjusting the frequency if you have
concerns of a Quirino toxicity consider
obtaining a vancomycin trough okay and
just to make sure the trough is in
raised before you give the next dose so
that's when you're gonna hold the dose
until you get the results of the trough
and also you could assess patients
you're an output
okay that's possible if the patient is
not making a lot of urine you're
probably not clearing the medication
either so regardless of what you get for
let's say the some Cayenne and or cran
and Clarence if the patient is not
making urine
you should probably dose adjust also
decrease the dose decrease the frequency
if you have to please note that the
serum creatinine trend rule also applies
for cran and Clarence also like before
you verify the medication or you're
monitoring these patients look for the
indication as this will help you
determine the duration of the vancomycin
also you could see the cultures that was
taken um that will also help you when
you're monitoring or working of these
patients for rounds alright just check
to see if you're using the vancomycin
for the right purposes right for the
right bug and that's all you really have
to do now I have some patient cases here
Patient Case 1
and these cases will allow you to like
develop the thought process when you're
evaluating a patient on vancomycin okay
well before you verify a vancomycin
order this is a male patient we have the
weight and the age here for you this is
the right GFR let's just say cran and
Clarence and Assam cannon and this
vancomycin was started on April 1st
right and this is the dose here 1.25
grams every 12 hours to be infused over
one hour the indication is sepsis and
the patient has received one to three
doses now based on the patient's weight
and age I agreed at one point to five
grams q 12 is appropriate right it's not
always think of one gram q 12 as kind of
like the baseline for like that the
average patient in terms of age and
weight one gram q 12 okay and just work
from there so this patient is you know
younger a little heavier so yeah they
could definitely get one point two five
grams every 12 hours
okay now the dose of frequency is
appropriate like I said the trough is
due before the fourth dose right in this
case on April 2nd and they're gonna aim
for 15 or 20 because the patient is
septic and you want to monitor the same
crannis since it's increased slightly
right 0.9 it's a 1.1 it may not be
significant now right but just keep your
eye on it if it goes up it's a chance it
might go up a little bit more right so
just just monitor for that so for
Patient Case 2
patient case 2 as we see right away you
know the renal function is very poor
this is a female he has the weight the
age and this patient was starting
vancomycin right it started on for one a
prefers vancomycin one gram every 24
hours for pneumonia now it's a good try
before the April 4 dose and they got 9.4
the initial dose could have also been
oh dear oh but not too old they yeah
yeah kind of heavy right you're kind of
on the high end in terms of the weight
and the renal function right when they
started on for one was 3.7 so just taken
taken into consideration just the renal
function and the age alone right the
serum cannon you could have probably
done 750 also but as you can see the
patient's renal function started to
improve a little bit so the trough was
low now based on the trough what do you
want to do you could do you can increase
the dose
alright the patient's renal function is
actually Inc like improving you can
increase the dose to 1.25 grams all 1.5
grams every 24 hours alright but you
want to be more conservative as a
pharmacist and I would probably go with
the 1.25 grams
once daily in this case right and just
monitor the renal function the renal
function goes back up the next day you
probably want to decrease that back to
one gram all right just to be
conservative is if it keeps dropping
leave it at 1.5 grams but if a job so
significantly let's say it's less than
less than one right then you just you
have more room right so you know
increase the dose if you need to patient
Patient Case 3
case 3 is a female here's the way age of
levels are here looks okay in terms of
the trend the patient started on a
prefers vancomycin one gram every 24
hours to be infused over one hour this
was a skin infection it's in the trough
before the April fourth dose and the
level was 18.9 so the initial dose is
acceptable in this case right based on
the patient's weight and age you know
patient is you know old you're not that
heavy right and the arena function is
not that great alright so you can just
give them one gram just once daily the
frequency is also okay based on the
renal function trough is high for the
indication
a skin infection if it's not really
touching the bone we usually aim for 10
to 15 the trough is high for that
indication so those could be decreased
around there for patient case four we
Patient Case 4
have a male who's 67 kilos 81 years old
receiving vancomycin 750 once daily to
be infused over one hour for skin
infection and here we have the serum
creatinine Tran and it seems like it's
increasing so it seems like this patient
is experiencing an acute kidney injury
and it may be appropriate to those this
patient buy levels in other words we
want to obtain a random vancomycin level
before each dose so the patient got the
four four dose right for the four five
those you wanna check the trough right
you want to get the level before you
give that dose but what we're gonna do
since the patient's renal function is
not doing good let's say it increased
also the next day we want to hold that
those on so we get the level back once
we get the level if the level is in
range all right then we might skip the
dose all right we don't need to give it
if it's elevated elevated we might we
definitely are gonna skip the dose if
it's low we are gonna give the dose okay
if it's in range you really have a
option to either hold it or actually
give it really depends you know if you
really feel like the renal function is
gonna improve or just check the level
alright just check the level of the
level is in range and you know the
patient is making urine or whatever the
case is all right you got to leave you
got to use your clinical judgment in
that case there's no right or wrong
answer in that case if like I said the
renal function continues to worsen the
next day I obtain another level before
uses before each dose just make sure the
patient only receives at those where the
trough is less than 20 patient case
Patient Case 5
number five this is a male who's eighty
two point one kilos 30
one-years-old we have the renal function
here seems okay they started this
patient on 1.25 grams every 12 hours for
skin infection they took the trough
right was taken before the fall for dose
and the level was five point for this
patient is young right kind of heavy the
trough is low so that those can be
increased to 1 point 5 gram every 12
hours I monitored the renal function
closely all right the patient's we know
function went up a little bit but went
back down but still just keep your eye
on it because the patient is on such a
high dose of the vancomycin now based on
the age the weight and the renal
function patient could have actually
even receive 1.5 grams every 12 hours as
the initial dose now this is a female
weighed 45 kilos 63 years old and here's
the renal function vancomycin one gram
every 12 hours we'll start on this
patient for skin infection once again
seems like what these patients have skin
infections right the dose is technically
okay for this patient based on the age
weight and renal function but the
patient's weight is on the lower end
right I would say in terms of weights
and the age is kind of on the high end
not 200 therefore you could have
technically and you could have been
conservative and started a patient on
you know just check the trough and go
based off that oh this is actually case
Patient Case 7
number seven so in this case we have a
male who is 98 kilos 49 years old and
here's the renal function also okay it
looks like it went down but then it went
back up right went up by 0.4 but then it
remained consistent for the next day and
this patient is getting vancomycin 1.25
grams every 12 hours to be infused over
one hour assuming you saw this order
before was verified
patient is heavy and not too older those
is okay but in this case the renal
function you just need some haunted
adrenal function right the dose is
definitely appropriate just make sure
the renal function that goes back down
this patient is really heavy and the
actually young you know so they could
they could probably take 1.25 grams with
no problem mainly because of the weight
and the patient is young on me yeah I
mean I know the renal function is at one
point three but it's 56 so there's a
chance of my improve right you give the
patient one dose let's say let's say the
patient only received one dose right
then when it got to fall for the renal
function got worse so the same cran was
like 1.6 right you could but you could
do in that case it seems like it's
getting worse right 0.9 1.3 1.6 is going
up you could check the level if you want
right or you could decrease this dose to
really an art there's no textbook way to
do this you know you gotta really use
your clinical judgment when you're
dosing these patients so just try to
think of the average patient as one gram
every 12 hours and then go on from there
to see if you should increase the dose
or decrease the dose and usually
sometimes you don't even know right with
the initial dose sometimes you may be
completely wrong
okay so just keep that in mind and try
to use your clinical judgment when it
comes to dosing vancomycin it should be
it should come naturally right because
it just makes sense
younger patient gets more have your
patients get more right all the patients
get less renal function code check level
right so you do everything based on the
trough really so don't be scared to ask
for a trough and always keep your eye on
the serum creatinine so that's the end
of this video I hope you guys enjoyed it
I hope I was able to you know explain
this in the best way to make
feel comfortable when it comes to
vancomycin and how we go about it in
clinical practice because in clinical
practice is definitely different from
what you learn in the textbook so notice
how I didn't calculate any doses for
these patients right I didn't use that
sense of 15 milligrams per kilogram I
just used my clinical judgment based on
the patient's age the patient's weight
to determine what those might be
appropriate so that's how you should
want to approach everything that you
learn in the textbook you want to bring
in so you know clinical practice and
just approach it in that direction so
this video is helpful make sure it's a
like comment subscribe and share it so
it's somebody that could definitely
benefit from it and I would definitely
appreciate that so and so then I hope
you take care and I'll see you soon












Comments
Post a Comment